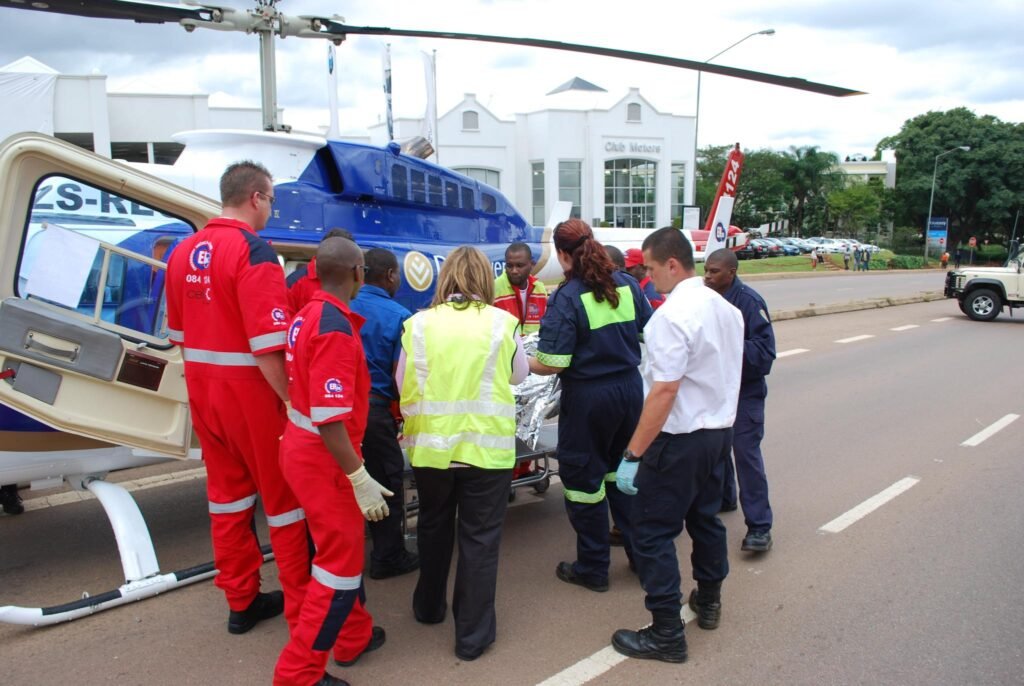
Emergency Medical Care When a health crisis strikes, every second counts. Whether you’re dealing with a heart attack, severe injury, or another life-threatening emergency, knowing what to do can mean the difference between life and death. This guide will walk you through how to identify medical emergencies, what immediate steps to take, and how to support emergency responders and healthcare professionals during critical moments.
Understanding Emergency Medical Care Situations
What Qualifies as a Medical Emergency?
A medical emergency is a sudden illness or injury that poses an immediate risk to a person’s life or long-term health. These include:
- Heart attacks
- Stroke
- Severe allergic reactions
- Heavy bleeding
- Seizures
- Breathing difficulties
- Unconsciousness
- Traumatic injuries (accidents, falls)
Recognizing these signs early allows for faster intervention and improves chances of survival.
Common Causes of Medical Emergencies
Medical crises can stem from various sources:
- Chronic diseases like diabetes or heart disease
- Accidents or trauma
- Allergies or adverse medication reactions
- Environmental factors (heatstroke, hypothermia)
- Poisoning or drug overdose
Step-by-Step Guide: What To Do During a Health Crisis
Step 1: Stay Calm and Assess the Situation

Remaining calm is crucial. Panicking can cloud judgment and delay necessary actions. Quickly assess:
- What happened?
- Is the person conscious or breathing?
- Is there any bleeding or visible injury?
- Are others around who can help?
Step 2: Call for Emergency Help
Once you identify that it’s a medical emergency, call emergency services immediately. Be ready to provide:
- Exact location
- Nature of the emergency
- Condition of the person
- Your contact information
Do not hang up until told to do so.
Step 3: Perform First Aid If Trained
While waiting for help, administer first aid if you’re trained:
- CPR for someone not breathing
- Heimlich maneuver for choking
- Pressure on wounds to stop bleeding
- Place in recovery position if unconscious but breathing
- Epinephrine auto-injector for anaphylaxis
Step 4: Avoid Harm and Ensure Safety
Ensure the area is safe for both the victim and yourself:
- Turn off stoves or electrical sources
- Move away from fire or water
- Clear the area of dangerous objects
Do not move the person unless there’s an immediate danger.
Emergency Care for Specific Conditions
Heart Attack
Symptoms: Chest pain, shortness of breath, pain in arms/jaw/back, cold sweat, nausea.
Action:
- Call emergency help
- Keep the person calm and seated
- Offer aspirin if not allergic
- Monitor breathing and prepare for CPR
Stroke
Symptoms: Sudden numbness, confusion, trouble speaking, loss of balance, severe headache.
Action:
- Use FAST: Face drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulty, Time to call help
- Do not give food or drink
- Keep the person comfortable and awake
Seizures
Symptoms: Jerking movements, unconsciousness, confusion, loss of control.
Action:
- Protect from injury (clear objects around)
- Do not restrain or put anything in the mouth
- Time the seizure
- After seizure, place in recovery position
Bleeding and Wounds
Action:
- Use a clean cloth to apply firm pressure
- Elevate injured limb if possible
- Do not remove embedded objects—stabilize them instead
Preparing for Health Crises in Advance
Build a First Aid Kit
Your kit should include:
- Bandages, gauze, antiseptic wipes
- Tweezers, scissors, gloves
- CPR mask, thermometer
- Pain relievers, antihistamines
- Emergency contact numbers
Learn Basic First Aid and CPR
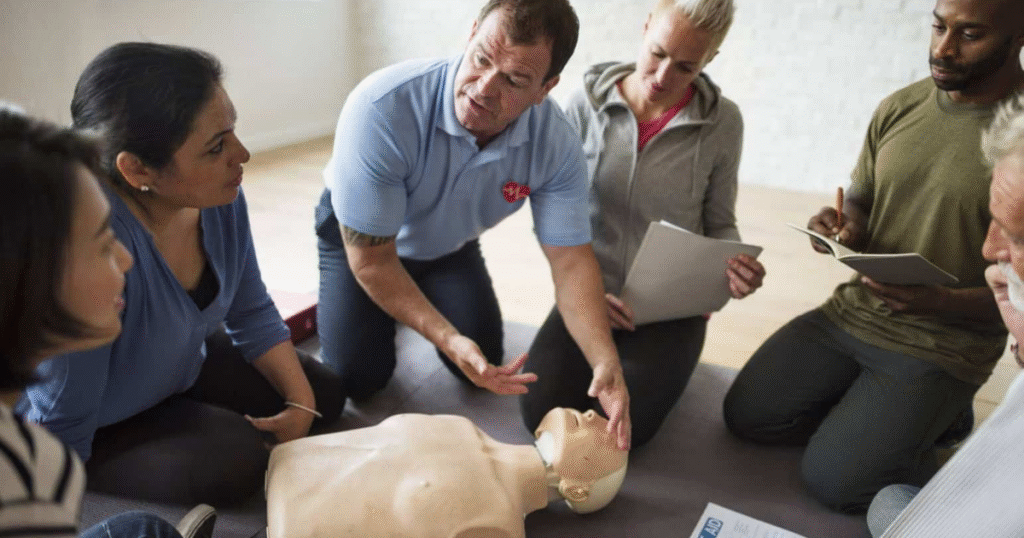
Training empowers you to take action confidently. Online and in-person courses are available and can be life-saving in emergencies.
Maintain Medical Information
Keep an updated list of:
- Allergies
- Current medications
- Medical conditions
- Emergency contacts
This should be accessible to family members or roommates.
Supporting Emergency Responders
Provide Clear Information
Stay composed when responders arrive. Share:
- What happened and when
- Symptoms observed
- First aid given
- Any medical history known
Follow Instructions Precisely
Responders are trained professionals. Cooperate and follow their directions, even if the situation feels chaotic.
After the Emergency: What Comes Next?
Hospital Care and Follow-Up
Once stabilized, the person may need:
- Hospitalization
- Diagnostic tests
- Surgical intervention
- Rehabilitation or therapy
Emotional and Mental Health Recovery
Witnessing or experiencing a crisis can be traumatic. Consider:
- Counseling or therapy
- Talking with loved ones
- Journaling or relaxation techniques
Emergency Medical Care for Children and Elderly
Children
- Keep calm; your reaction affects them
- Use child-appropriate CPR methods
- Know signs of choking or poisoning
Elderly
- Be aware of chronic conditions
- Watch for falls or strokes
- Understand the side effects of medications
Remote Areas or No Access to Immediate Help
Use Emergency Communication Tools
If you’re in an area with no cell service:
- Use satellite communication devices
- Carry emergency radios
Temporary First Aid Solutions
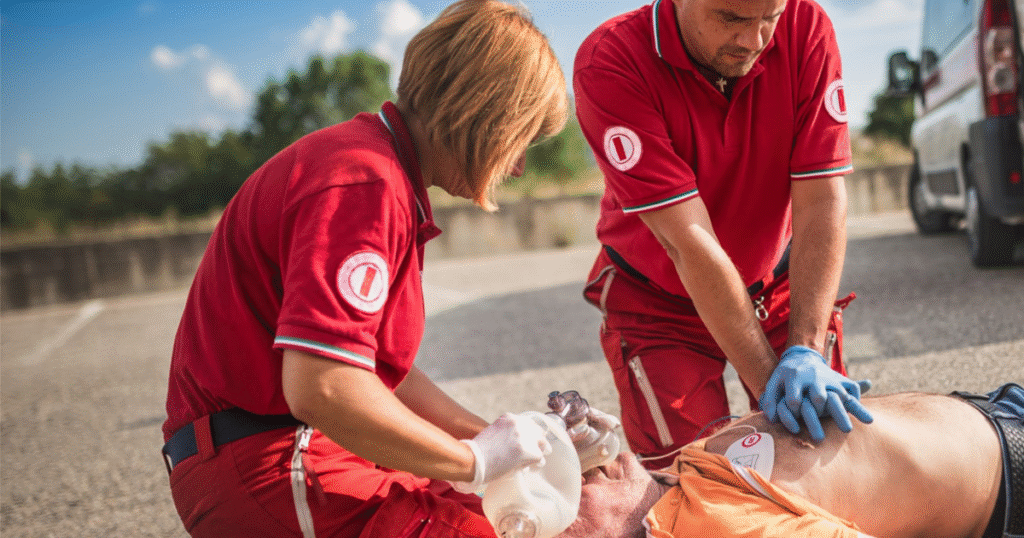

- Make improvised splints or dressings
- Use pressure to stop bleeding
- Keep the injured warm and hydrated
Importance of Staying Updated
- Re-certify in CPR and first aid regularly
- Update emergency kits every 6 months
- Review evacuation plans and emergency numbers
Also Read : The Science Of Gene Therapy: Unlocking The Secrets Of DNA!
Conclusion
Being prepared for a medical emergency is not just about having a first aid kit—it’s about having the knowledge and presence of mind to act fast and appropriately. Recognizing early signs, calling for help promptly, and administering correct first aid can save lives. With training, preparation, and awareness, anyone can become a crucial link in the chain of survival during a health crisis.
FAQs
1. What is the first thing I should do in a medical emergency?
The first step is to remain calm, assess the situation, and immediately call emergency services if someone is seriously injured or ill.
2. Should I attempt CPR if I’m not trained?
If untrained, emergency dispatchers can guide you through “hands-only” CPR until help arrives. It’s always best to take a certified CPR course.
3. Can I give medication to someone in an emergency?
Only administer medication (like epinephrine or aspirin) if you are certain of the person’s medical history and allergies. Avoid giving anything unless necessary and safe.
4. What should I do if a child is choking?
Give age-appropriate back blows and abdominal thrusts. For infants under 1 year, use back slaps and chest thrusts instead.
5. How often should I update my first aid kit?
Every 6 months. Check for expired medications, used items, or damaged equipment.
